Making a Pattern for Fabric Collage: Fabric Collage By the Numbers #3
This post continues our DIY Summer Collage Camp—or a Winter Collage Camp for those of you in the Southern Hemisphere. We’re calling it “Fabric Collage By the Numbers,” addressing all the steps of creating a fabric collage quilt. We hope you’ll participate from wherever you are in the world—no travel involved!
Pulling from six and a half years of fabric collage blog posts as reference material, we are delving into that content to give you a summertime lineup that you can follow along with. At the start of this series, there were eight weeks left of summer (not by the calendar but by the very subjective lens of the Maine climate!) so each week we’ll deliver two posts for a total of sixteen in the series—unless we re-discover more relevant posts along the way!
Posts will include; #1 choosing your photo (posted on July 7), #2 choosing a subject (posted on July 9) to eventually hanging your fabric collage on the wall (planned delivery on August 27), we’ll cover each step with at least one previous post.
While today’s primary #3 post is all about “Making a Pattern for Fabric Collage,” I also want to draw your attention to another past post: “The Topography of the Fabric Collage Face,” published on January 30, 2021. This post may help you to see your subject from a slightly different point of view. Whether it is a human face or a giraffe’s snout, understanding the underlying 3-dimensional “topography” of a face, or any part of your subject, can certainly help in creating a 2-dimensional pattern to base the rest of your fabric collage on.
You may have read some of these posts before, so this will be a refresher for you. The information may also be reminiscent of information found in our online learning resource the Fabric Collage Master Class. If so, know that you’re not imagining things. Much of this information is gathered, reorganized and expanded upon in the Master Class. For more information about the Fabric Collage Master Class, click the button below.
Making a Pattern for Fabric Collage
UPDATE (Published on February 18, 2017)
As promised, I’m selecting some of the most popular posts from my blog and updating them with video—something that elaborates on or shows more detail in the fabric collage technique. Starting with the most popular posts—the ones that have been viewed, shared, and commented on the most—this is now the second installment of the “Update Series.”
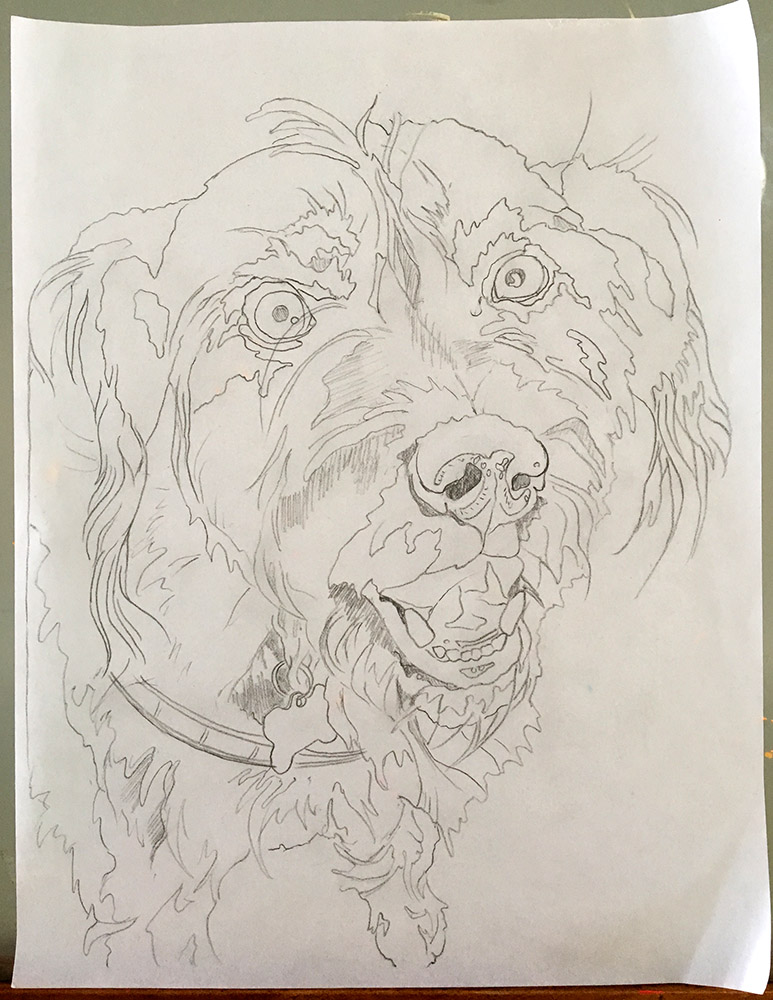
This particular post originally began and ended with drawings of a past pup of ours (Pippin), so I choose an image of a current pup, Felix, to demonstrate via video the pattern drawing process.
Felix is a dark dog–an easy description would be dark grey–not an easy subject to photograph. Add to that his camera shyness and we have many pics of him as a dark blur. So imagine my delight when a beautiful sunset walk at the end of the peninsula we live on yielded a sun-soaked photo of our wonderfully shaggy three-legged happy dog.
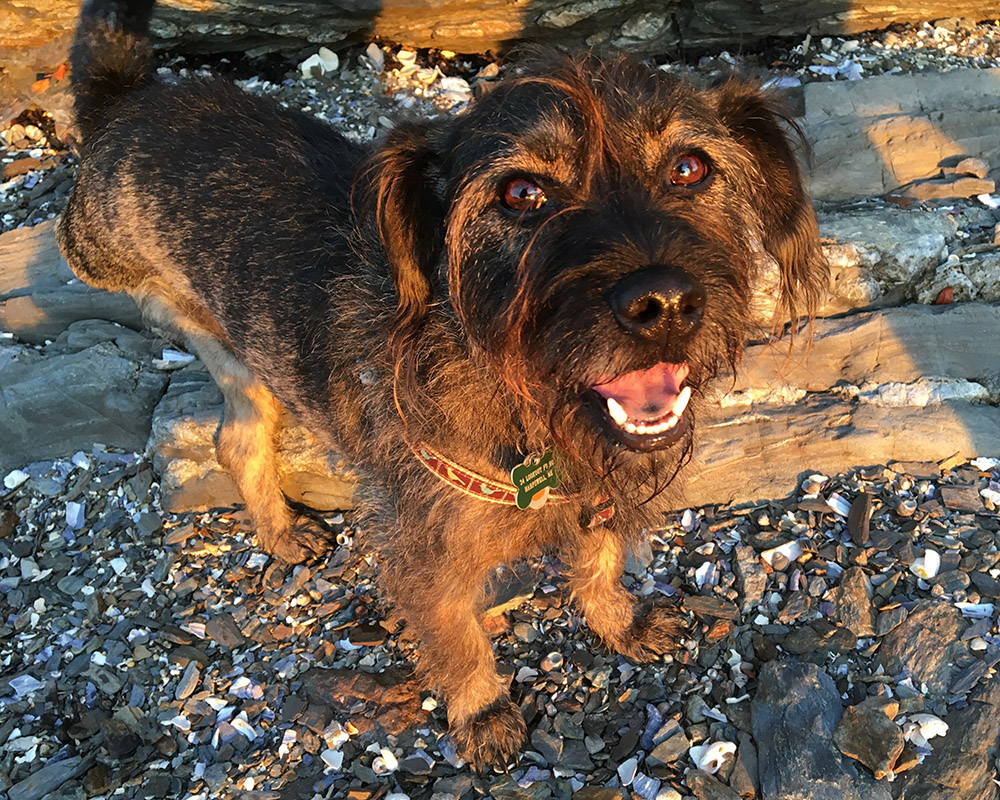

This photo accented the few browns on his face and gave me the highlights and shadows I would need in creating the line-drawing for the pattern, as well as definition to his face and body to guide me later in the collage process itself.
As I say in the original post, in creating a line drawing, I begin by looking for the lights and darks of the image. I outline those areas, taking care to be as accurate as I can. This might take me a while, but I find that time spent looking at, drawing, and generally familiarizing myself with my subject is in no way wasted. The more ways I can put the image into my brain, the better. I think it helps all along—from design to fabric selection to the collage process itself.
And here—tah dah!—is your video. Enjoy.
ORIGINAL POST (First published on April 2, 2016)

So you want to make a fabric collage quilt. Great!
After choosing an image to work from, the next step in creating a fabric collage quilt is making a simple pattern. This is a critical step, one that even beginning students sense has an enormous influence on the success of their finished product. Knowing how much is riding on creating a suitable pattern makes this a daunting task to the beginner.
It doesn’t need to be scary.
The basic steps are simple:
- Enlarge selected image to letter size: 8½ x 11 inches.
- Use tracing paper to outline shapes based on value.
- Enlarge tracing to desired size of completed quilt.
- Transfer outline to foundation fabric.
Okay, so you can go deeper than that, but that’s the basics. Let me elaborate by using a few of my own quilts as examples.
To see final versions of the quilts: “Kissing Cousins” is featured in a previous blog post: A Christmas Gift that Keeps on Giving. “Peace, Love, Tie-Dye, Save the Whales” is featured in my blog post on value: Why Color Is Irrelevant. “Dixie Dingo Dreaming” can be viewed on my website.
Step One: Enlarge selected image to letter size: 8½ x 11 inches.
Letter size is nice because it’s convenient. Most people have home printers nowadays, so it’s easy to print out an image as big as will fit on a regular piece of paper.

Why not bigger? Why not print out the image at the finished size? That seems logical. The bigger you print it out the easier it is to see details, right? That might be true if you have an extremely high resolution image. But the resolution on most personal and cellphone cameras just isn’t that great. If you blow up an image too much, you’ll actually lose detail.
Keep the original handy. You’ll be referring to it during the piecing process.

Extra credit: In order to draw out the differences between shades of value, you might try tweaking the brightness and contrast in a image manipulation program such as Photoshop before printing out your image. You could also try turning it black and white, posterizing it, or playing with changing its colors. These all may help you see the image as a collection of values.
Step Two: Use tracing paper to outline shapes based on value.
Tracing vellum is nice and transparent, if you can find some, but regular old tracing paper will do if that’s what you have. Using a nice, sharp pencil (I like mechanical pencils for this), start outlining the larger shapes based not on, say, parts of a face—nose, mouth, eyes—but in terms of value. A nose will be made up of several shapes—dark, medium, and light areas. If you need a refresher on value, visit my blog post “Why Color Is Irrelevant.”


Resist the urge to be extremely detailed. It will simply be too confusing. Also, as you will see in the example of “Dixie Dingo” (below), the pattern will get covered up quite quickly, making all those details a waste of time. If it starts looking like a crazy paint-by-number drawing, then you probably have too much detail. Look for lightest areas and darkest areas to draw around. The middle values get filled in as the piecing process progresses.
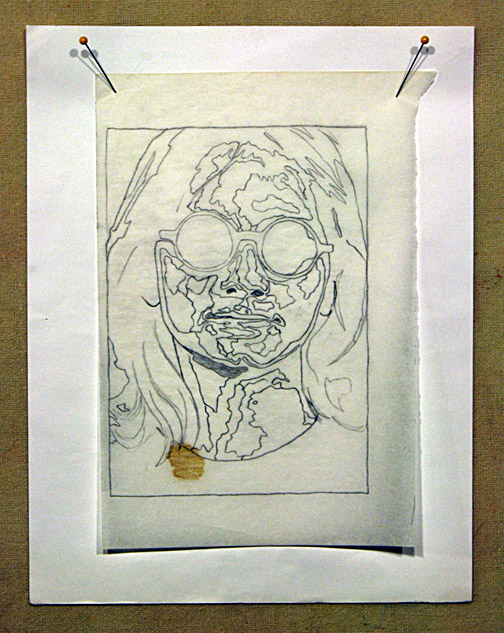




Extra Credit: Do simple shading in the darkest shapes to indicate shadows. A lighter shading can be added to shapes where the value is in the mid-tones. Leave the highlights white. This drawing, after you transfer it to the foundation fabric, can serve as a “cheat-sheet” of sorts and help you keep track of what values go in what shapes.
Step Three: Enlarge tracing to desired size of completed quilt.
When in doubt, go big. How big? One rule of thumb: a face should generally be at least 10 to 12 inches top to bottom. Even bigger is better. Imagine trying to create an eye the size of your pinkie nail. Now imagine it the size of a golfball. Make it easy on yourself and go bigger.

The easiest way to get your tracing enlarged is to take it to a local copy shop. Most big box business supply stores have a copy center. Tell them how big you want the finished pattern to be and let them do the math.
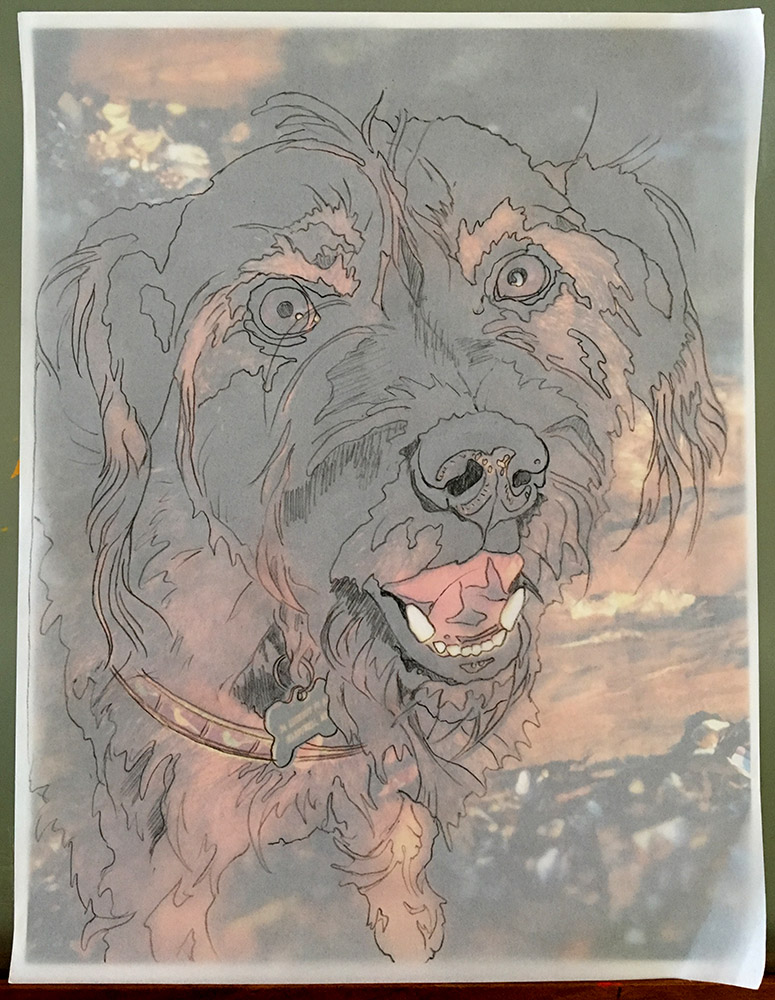
Another method is to enlarge it at home. This will require you to scan your tracing, then print it out at whatever percentage you desire. This will probably require you to “tile” the image together in several pieces. I do this with all my designs (see photo above and”Dixie Dingo” photo at beginning) since I have in-house copy service, a.k.a. Tom, my husband.
So how do you figure out what percentage to use? Simply divide the finished size by the original size then multiply by 100. It doesn’t matter which dimension, height or width, you use as long as you choose the same on both finished and original. Another way to figure out your enlargement is to use a proportion scale. And of course there are apps for that.
Step Four: Transfer outline to foundation fabric.
Choose a plain, regular weight fabric for the foundation that you’ll be gluing to. Muslin, or another inexpensive neutral colored fabric, works well. Cut a piece slightly bigger than your paper pattern. When you slip the pattern behind the fabric, you should be able to see it well enough to use a permanent marker (such as a Sharpie) to trace the image onto this foundation. You want a nice solid, definitive line. This is your guide and reference. There are no templates in the way I work.
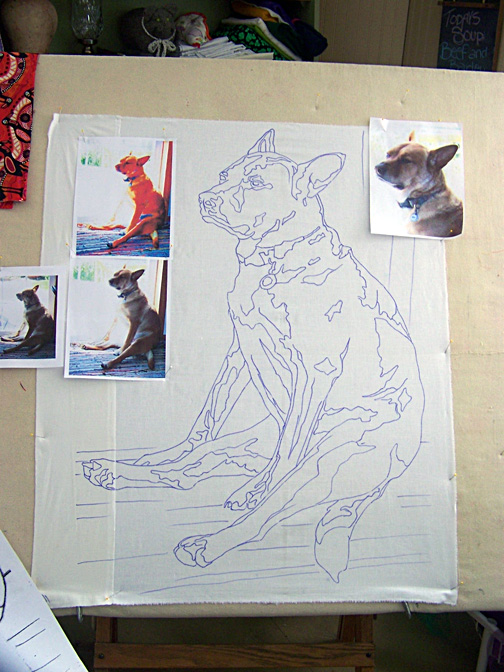

Extra Credit: If you shaded in the darker areas on your pattern, transfer those to the fabric as well.
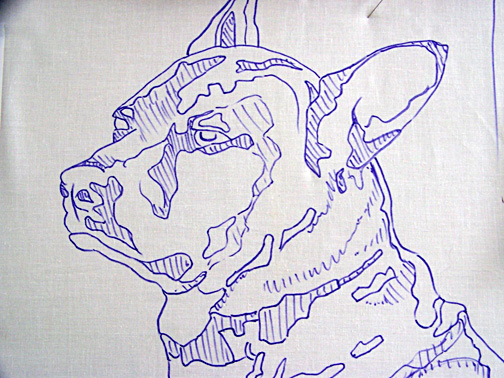

Final Exam
Students are often impatient to start creating their image in fabric, but don’t rush your pattern. Take your time. Maybe you’ll have to make a second draft, as I did with “Peace, Love, Tie-Dye, Save the Whales.” It’s well worth the effort at this stage to create an accurate pattern. As you move on to the the next step in the process—fabric collage piecing—a good pattern will ____________.
a. be the foundation on which your fabulous quilt will be built.
b. be your best friend.
c. give you extra confidence.
d. all of the above.



2 Comments